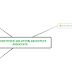
| Development Stage | What needs governance | How do we (or tools/techniques used for) govern? |
| Business Problem |
|
|
| Requirement Gathering |
|
|
| Architecture |
|
|
| Design |
|
|
| Implementation |
|
|
| Testing |
|
|
| Documentation |
|
|
| Deployment |
|
|
| Service / Maintenance |
|
|
19 Apr 2016
13 Apr 2016
How to Structure Essay writing to score High in IELTS PTE
Agenda
1. Understand the Type of the Question.
2. List the Scope
3. List the Idea
4. List out the keywords and vocabulary to use.
5. Develop the Format
6. ProofRead and Enrich.
1. Understand the Type of the Question.
Based on the question demands, identify whether it is
a. Discussion
b. Argument
2. List the Scope
As given in the question, identify scope of the article by listing 3-4 keywords.
Whole article has to revolve around these keywords.
3. List the Idea
a. Idea 1: For Para1 : Teachers can change the approach of teaching.
b. Idea 2: For Para2: Motivation, inspiration, discipline
c. Idea 3: For Comparing
4. List out the keywords and vocabulary to use.
Refer: http://surenova.blogspot.in/2016/04/top-9-linking-sentences-to-be-used-in.html
5. Develop the Format
6. Proof Reading:
Spelling, broken links, and vocabulary.
Example:
Technology has been increasingly used throughout the world. This is very apparent in classrooms today.It is disagreed that technology will replace the teachers in class room.
This will be proved by analyzing how teachers can crater to the needs of their students as well as motivate and discipline them.A very important aspect of teaching is ability of the teacher to shape their teaching style to the needs of their students.
As an example, If students in any give class are having trouble understanding a classroom topic, a teacher can rephrase the topic and deliver it in more effective way.
A computerized teacher would be less in-tune with what students require and thus would be incapable of doing this.
Thus, technology will not replace teachers.Motivation and disciple are key to student’s academic success in class room.
This is very apparent, when teaching children as children require more motivation and discipline to be taught effectively.Technology based teacher simply cannot accomplish this as certain situations demands judgement as to whether the student is acting in appropriate manner.
After analyzing, it is clear that the teachers will always be needed in the classroom.
Following the analyzation of the teacher’s ability to crater the students as well as their capability of guiding towards success,.
it is clear that technology will never replace teachers and class room
It is expected that , technology will act as a supplement to teachers.
210 Words.
Top 9 Linking Sentences to be used in Essays
1. “In order to understand X, we need first to understand Y.”
2. “Frogs are amphibians. In other words, they live on the land and in the water.”
3. “Moreover, the results of a recent piece of research provide compelling evidence in support of…”
4. “Furthermore, there is evidence to suggest that…”
5. The war caused unprecedented suffering to millions of people, not to mention its impact on the country’s economy.”
6. Scholar A thinks this. However, Scholar B reached a different conclusion
7.The historical evidence appears to suggest a clear-cut situation. On the other hand, the archaeological evidence presents a somewhat less straightforward picture of what happened that day.”
8. We may use this as evidence to support our argument, provided that we bear in mind the limitations of the methods used to obtain it.
9.“In conclusion, the evidence points almost exclusively to Argument A.”
3 Apr 2016
SOLID Principles

Single Responsibility Principle
There should never be more than one reason for a class to change.
Open Closed Principle
Module should be open for extension but closed for modification.
Eg: For existing 10 algorithm, if I have to add 11th algorithm it should allow for extension.
Liskov Substitution Principle
Functions which uses reference of base class, should be able to use objects of derived class without knowing them.
Eg: Program generic Interface, and do not refer concrete classes.
Interface Segregation Principle
Many client interface are better than one generic Interface.
Dependency Inversion Principle
High level modules should not depend on low level modules. Do not depend on many classes, depend on Interfaces or abstractions.
Both should depend on abstractions.
Abstractions should not depend on details.
Details should depend on details.
Program to interface, not to concrete classes.
Fundamentals in OOPS Concepts

Abstraction
focusing on essential characteristics of an object not all.
Encapsulation
which hides internal details of object.
Modularity
dividing cohesive and loosely coupled
Hierarchy
(is a)
(part of) – Aggregation
Containment
Aggregation(diamond)
Inner objects life-time is not controlled by outer object.
Containment
Inner objects life-time is controlled by outer object.
Polymorphism ( can be Aggregation
compile
runtime
Namespace
Logical naming and grouping
Inheritance:
It is white-box reusability. Concrete class can easily override the logic in base class.
Composition:
It is black-box resuse, when I am using the object, I get access its public property but not its private.
Design Patterns (Brief)

CREATIONAL ( Object Creation)
1. Factory Method
creating an instance of several of derived classes.
2. Abstract Factory
creating a family of classes.
3. Builder
Builds the object in parts. (step by step)
4. Singleton
Only one instance of an object to be created.
5. Prototype
Fully initialized object need to be copied or cloned.
STRUCTURAL
1. AdapterBEHAVIOURAL
Eg: different classes having different interface, we need adapter to match the interface of classes
2. Bridge
When product is sold , support team separating the developing team from customer.
3. Composite
is mainly involved in tree of Simple and composite (complex) objects.
4. Decorator
used to add responsibility to the object at runtime dynamically.
5. Proxy
used when you want an object to represent another object.
6. FlyWeight
used when a fine grained object to be used efficiently.
7. Facade
single class is representing sub-system. Abstract the complex structure.
1. Chain of Responsibility
while passing request to chain of objects.
2. Command
encapsulate the request in object
3. Interpreter
includes the language element in the program
4. Iterator
used when to take out traversal item in the list.
5. Mediator
When we want to simplify between two objects.
6. Memento
when we want to capture and restore (Eg: Undo operation)
7. Visitor
defines new operation to class without changing the class.
8. Template
differ exact steps to sub class.
9. Strategy
to encapsulate an algorithm in a class.
10. State
to alter object behavior only when its state change.
11. Observer
to notify the change to other objects, (publish and subscriber).