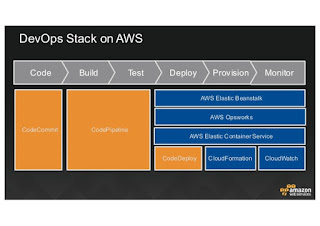
1. Uniform Interface


Individual resources are identified using URLS. The resources (database) are themselves different from the representation (XML, JSON, HTML) sent to the client. The client can manipulate the resource through the representations provided they have the permissions. Each message sent between the client and the server is self-descriptive and includes enough information to describe how it is to be processed. The hypermedia that is hyperlinks and hypertext act as the engine for state transfer.
2. Stateless Interactions

none of the clients context is to be stored on the server side between the request. All of the information necessary to service the request is contained in the URL, query parameters, body or headers.
3. Cacheable

Clients can cache the responses. The responses must define themselves as cacheable or not to
prevent the client from sending the inappropriate data in response to further requests.
4. Client-Server
The clients and the server are separated from each other thus the client is not concerned with the data storage thus the portability of the client code is improved while on the server side the server is not concerned with the client interference thus the server is simpler and easy to scale.
5. Layered System

At any time client cannot tell if it is connected to the end server or to an intermediate. The intermediate layer helps to enforce the security policies and improve the system scalability by enabling load-balancing
6. Code on Demand

an optional constraint where the server temporarily extends the functionality of a client by the transfer of executable code.